Longbow+
Longbow+ is an enhanced version of longbow. It is also used for long windowed aggregations. One of the limitations for longbow was the lack of support for complex data types. Longbow+ lets you select as many complex fields as required and it has its own DSL in place to query these complex fields. This currently works only for Kafka sink.
Components
Similar to longbow, longbow+ also has the following components.
But unlike longbow, the above two components are divided into multiple daggers instead of a single one. The main idea behind dividing this into two daggers is to resue the data published by longbow_writer by multiple longbow_reader for different use cases. In order to connect the two daggers, longbow_writer publishes a synchronization log having some metadata that can be consumed by multiple longbow_reader daggers. From the output of a longbow_reader, different daggers can be used in order to query the historical information as explained here.
Longbow writer#
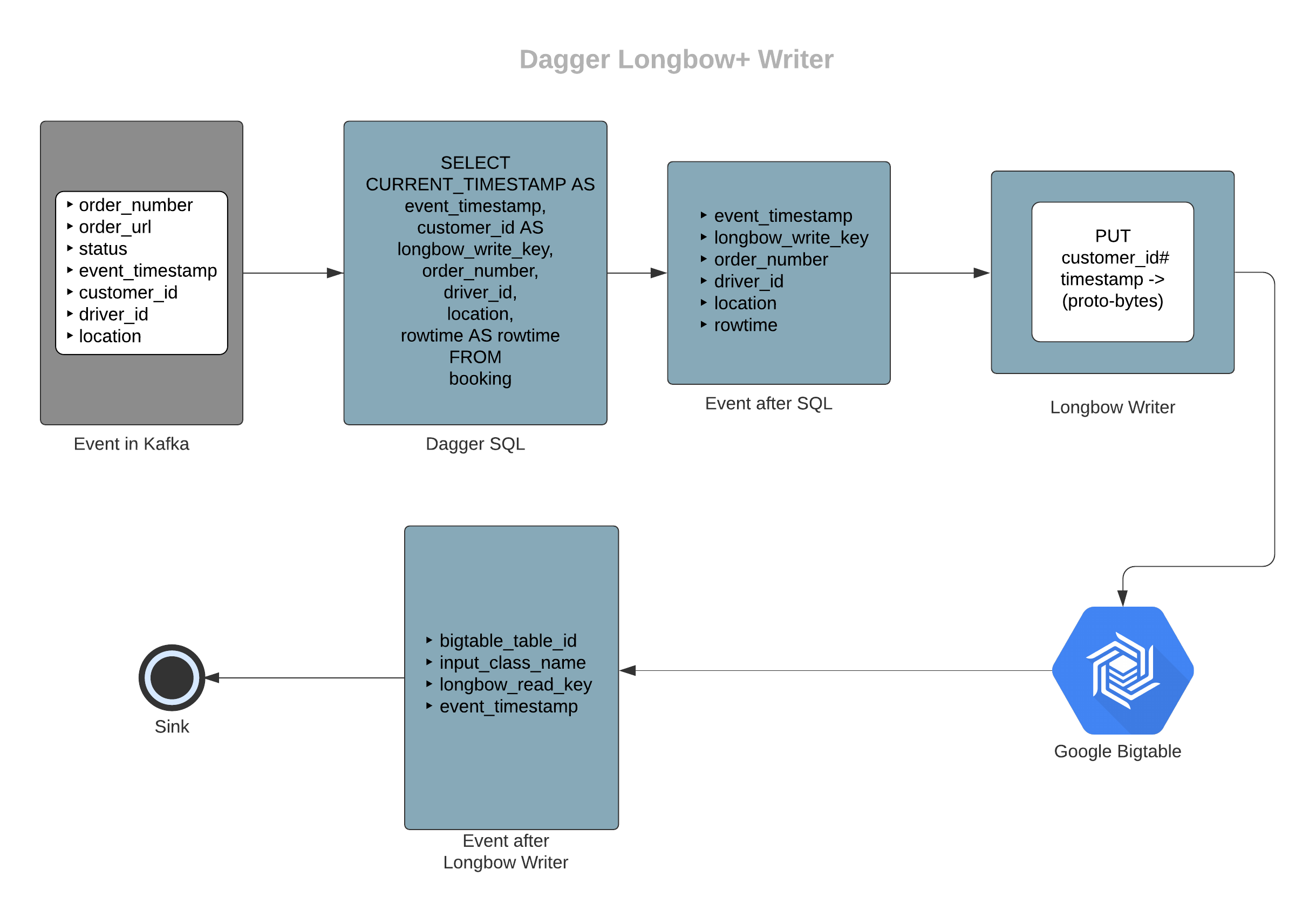
LongbowWrite has two responsibilities, to write an incoming event to BigTable and then emit a resultant event containing metadata(like table name, input proto class name, longbow key, etc.) to a Kafka topic after each successful write. It uses Flink's Async IO in order to make the network call.
Workflow#
- Create a new table(if doesn't exist) with the name same as Dagger job name or using PROCESSOR_LONGBOW_GCP_PROJECT_ID.
- Receives the record post SQL query processing.
- Creates the Bigtable key by combining data from longbow_write_key, a delimiter, and reversing the event_timestamp. Timestamps are reversed in order to achieve lower latencies in scan query, more details here.
- Creates the request by serializing all the remaining values(i.e apart from fields passed as configs) from SQL query using the
INPUT_SCHEMA_PROTO_CLASSproto, and adding the serialized bytes in a single Bigtable row column named asproto. - Makes the request.
- Passes the row after adding additional metadata fields like input_class_name, bigtable_table_id, longbow_read_key to the sink.
- Configured Kafka sink publishes the data to Kafka.
Note: By default we create tables with retention of 3 months in Bigtable.
Example#
In this example, let's assume we have booking events in a Kafka cluster and we want to get information of all the order numbers, their driver ids and location(complex field) for customers in the last 30 days. Here customer_id will become longbow_write_key.
Sample input schema for booking
message SampleBookingInfo { string order_number = 1; string order_url = 2; Status.Enum status = 3; google.protobuf.Timestamp event_timestamp = 4; string customer_id = 5; string driver_id = 6; Location location = 7;}message Location { double latitude = 1; double longtitude = 2;Sample output schema for longbow writer output
message SampleLongbowSynchronizer { string bigtable_table_id = 1; string input_class_name = 2; string longbow_read_key = 3; google.protobuf.Timestamp event_timestamp = 4;}Note: The longbow_write_key is populated as longbow_read_key in the output topic in order to pass the key to longbow_reader.
Sample Query
# here booking denotes the booking events stream with the sample input schemaSELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP AS event_timestamp, customer_id AS longbow_write_key, order_number, driver_id, location, rowtime AS rowtimeFROM bookingIn the above example, customer_id along with a delimiter and reversed timestamp will form the Bigtable row key. Values of order_number, driver_id and location will be serialized using SampleBookingInfo proto and will be inserted under proto column in the Bigtable row.
Configurations#
Longbow+ writer is also entirely driven via SQL query like longbow, i.e. on the basis of the presence of certain columns we identify longbow+ writer parameters. Following configs should be passed via SQL query as shown in the above example.
longbow_write_key#
The key from the input which should be used to create the row key for Bigtable. Longbow+ writer will be enabled only if this column is present.
- Example value:
customer_id - Type:
required
event_timestamp#
The timestamp to be used to build the Bigtable row keys.
- Example value:
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP - Type:
required
rowtime#
The time attribute column. Read more here.
- Example value:
rowtime - Type:
required
Longbow+ writer utilizes same global longbow configs. Details here.
Longbow reader#
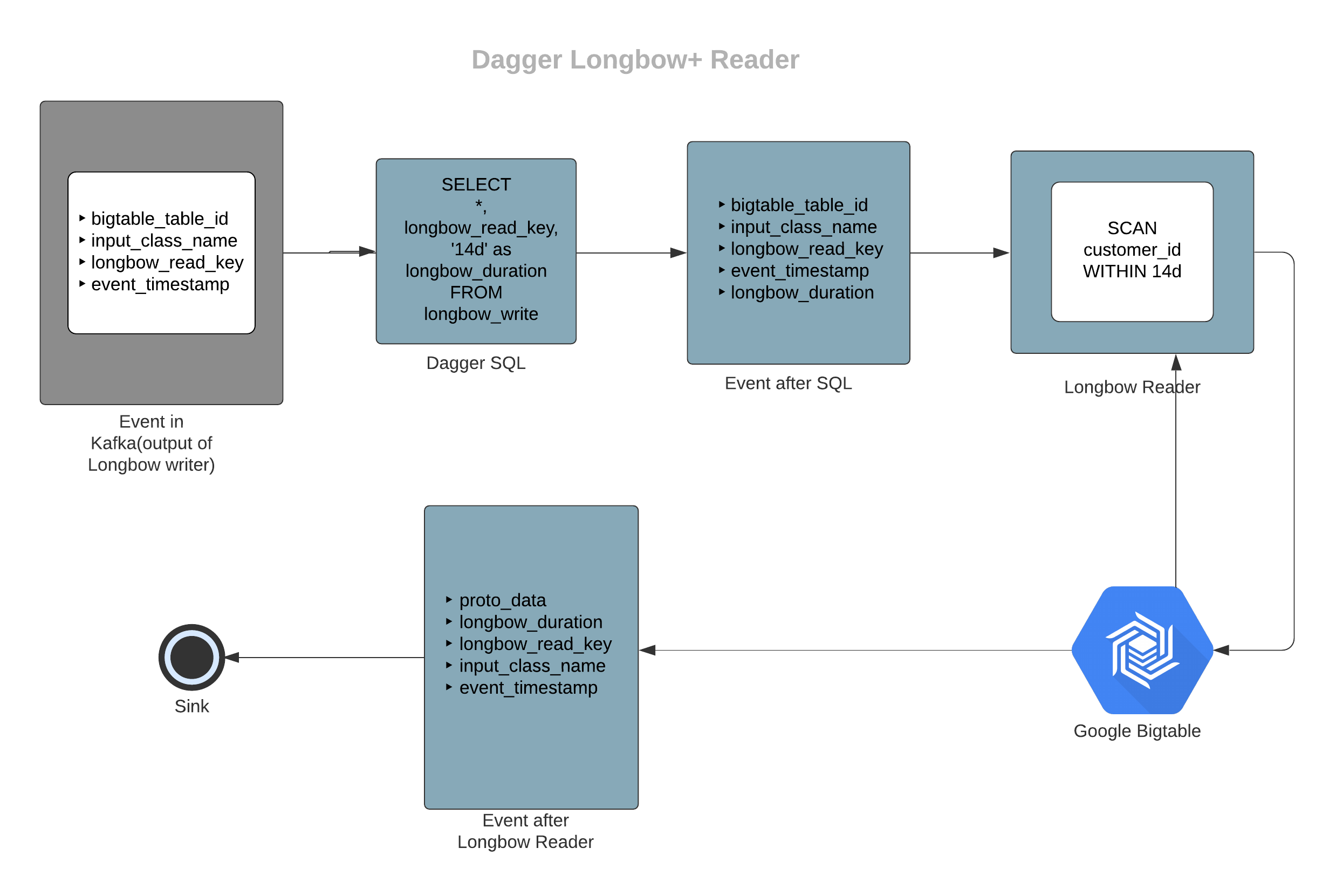
It reads the output of LongbowWrite and fetches the data for a particular key and a time duration from BigTable. It creates accumulative data for a configurable duration for other Daggers to use. It pushes the result along with some metadata to another Kafka topic. It also uses Flink's Async IO in order to make the network call.
Workflow#
- Reads the output of LongbowWrite from Kafka topic.
- Figures out the Bigtable row key from
longbow_read_keycolumn value. - Builds the scan request for Bigtable. We provide two configurable strategies for defining the range of the query.
- Duration range: It will scan from the latest event's timestamp to a provided duration.
- Absolute range: You can provide the absolute range by setting longbow_latest and longbow_earliest in the SQL query.
- Makes the scan request and receives the result.
- Parses the response and creates a list of values and adds them to
proto_datacolumn in the output. Thus every record post this stage will have its historical data within the same record. - Forwards the data to the sink.
Example#
In this example, we are consuming the output from the longbow_writer example mentioned above.
Sample output schema for longbow reader output
message SampleLongbowReaderOutput { repeated bytes proto_data = 1; string longbow_duration = 2; string longbow_read_key = 3; string input_class_name = 4; google.protobuf.Timestamp event_timestamp = 5;}Sample Query
# here longbow_write denotes the events stream with the longbow writer outputSELECT *, longbow_read_key, '14d' as longbow_durationFROM longbow_writeIn the above example, proto_data field will contain a list of all the historical messages.
Note: Select longbow_read_key explicitly in the query (even if you have selected *).
Configurations#
Longbow+ reader is also entirely driven via SQL query like longbow, i.e. on the basis of the presence of certain columns we identify longbow+ reader parameters. Following configs should be passed via SQL query as shown in the above example.
longbow_read_key#
The key using which Bigtable scan row keys will be created. Longbow+ reader will be enabled only if this column is present.
- Example value:
customer_id - Type:
required
event_timestamp#
The timestamp to be used to build the Bigtable scan row keys.
- Example value:
created_at - Type:
required
rowtime#
The time attribute column. Read more here.
- Example value:
rowtime - Type:
required
Longbow+ reader utilizes same global longbow configs. Details here.
Using longbow reader output#
Given that the output of longbow_reader will contain a list of bytes, it becomes hard to use it directly in the SQL query. So we added a few custom UDFs in order to make this easy for the users. These UDFs simplify the Dagger query for consuming data from longbow reader. They consume the data which is in the form of bytes and do deserialization and filtering/field selection on top of it.
Field Selection#
You can use SelectFields UDF for this. You can select one of the fields from the output of longbow reader and either use it in the query or send it downstream for other systems to use. It returns an array of the selected data type.
Filtering#
You can use Filters UDF for this. This function is used with predicates that decide what data to keep. One example of the predicate is CondEq. You could use one or more predicates to filter data as per your requirements.
CondEq#
One of the predicates to be used in Filters. This predicate allows you to equate the field with a specific value. Ex:CondEq(‘status’, ‘Completed’) helps filter function to filter data where status is completed. More info here.
Note: It supports String, Integer & Boolean data type.
Sample Query#
# here longbow_read denotes the events stream with the longbow reader outputSELECT ArrayAggregate( SelectFields( proto_data, input_class_name, 'order_number' ), 'distinct.count', 'Other' ) as distinct_ordersFROM longbow_readWHERE cardinality( SelectFields( proto_data, input_class_name, 'order_number' ), 'distinct.count', 'Other' ) ) > 20In the above query, we are outputting the number of distinct order_number where it is greater than 20.