Architecture
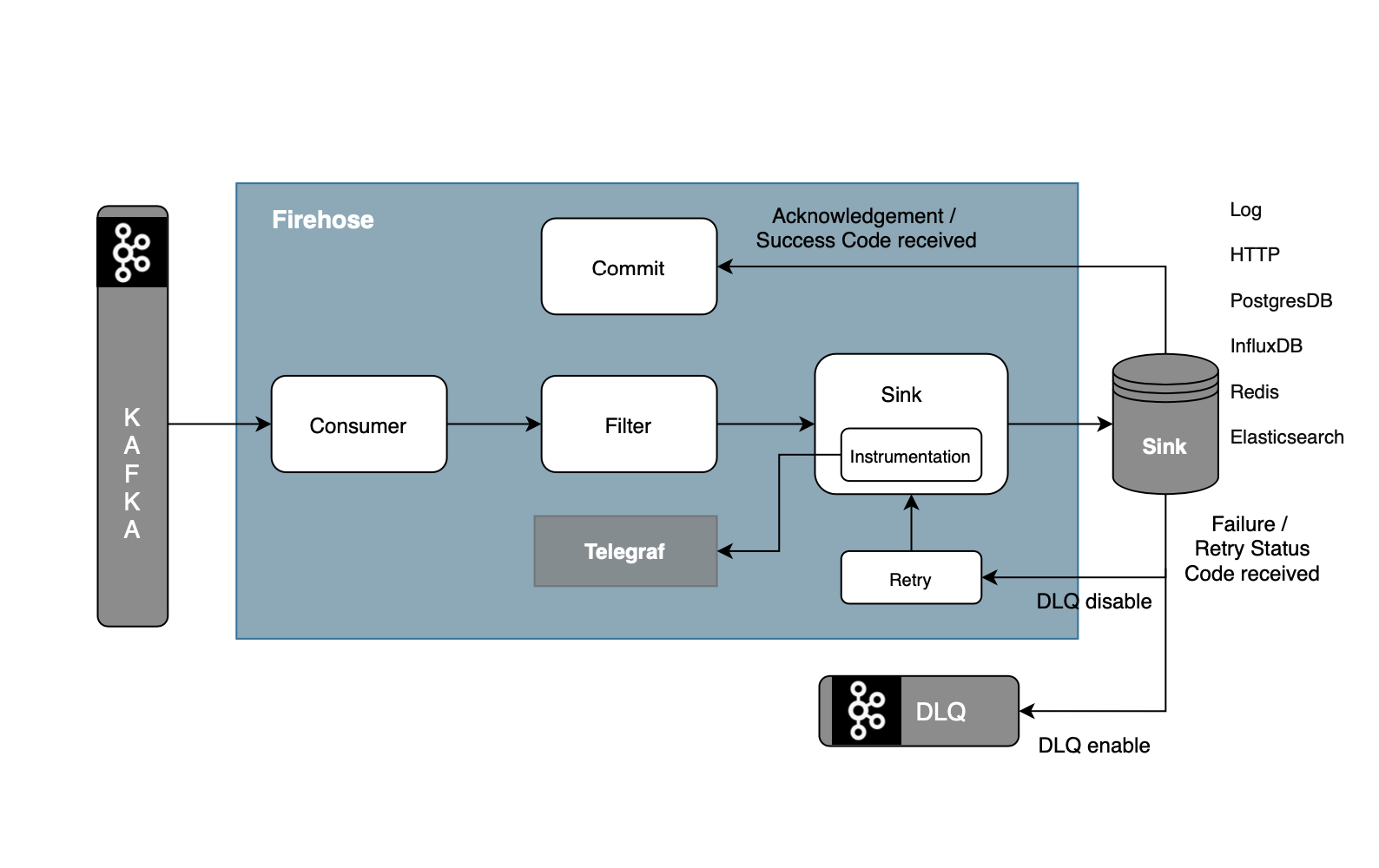
Firehose has the capability to run parallelly on threads. Each thread does the following:
- Get messages from Kafka
- Filter the messages (optional)
- Messages are processed by a chain of decorators, each decorator calling the previous one and processing the returned result.
- Push these messages to sink.
- Process the messages not pushed to sink by chained decorators.
- Fail if the error is configured.
- Retry if the error is configured.
- Push to DLQ if the error is configured.
- Ignore messages.
- Captures telemetry and success/failure events and send them to Telegraf
- Repeat the process
System Design
Components
Consumer
- Firehose supports sync and async consumers.
- Sync and async consumers differ in their kafka offset commit strategy.
- SyncConsumer pulls messages from kafka, sends to sink and commits offsets in one single threads. Although Sink can choose to manage its own offsets by implementation appropriate methods. Consumer will get offsets from the sink while committing.
- AsyncConsumer pulls messages from kafka, submit a task to send messages to SinkPool, tries to commit the kafka offsets for the messages for which the tasks are finished.
Filter
- Here it looks for any filters that are configured while creating Firehose.
- There can be a filter on either Key or on Message depending on which fields you want to apply filters on.
- One can choose not to apply any filters and send all the records to the sink.
- It will apply the provided filter condition on the incoming batch of messages and pass the list of filtered messages to the Sink class for the configured sink type.
Sink
- Firehose has an exclusive Sink class for each of the sink types, this Sink receives a list of filtered messages that will go through a well-defined lifecycle.
- All the existing sink types follow the same contract/lifecycle defined in
AbstractSink.java. It consists of two stages:- Prepare: Transformation over-filtered messages’ list to prepare the sink-specific insert/update client requests.
- Execute: Requests created in the Prepare stage are executed at this step and a list of failed messages is returned (if any) for retry.
- Underlying implementation of AbstractSink can use implementation present in depot.
- If the batch has any failures, Firehose will retry to push the failed messages to the sink
SinkPool
- Firehose can have a sinkpool to submit tasks based on the configuration. SinkPool is used to asynchronously process messages.
- SinkPool is defined by number of threads and poll timeout of the worker queue.
Instrumentation
- Instrumentation is a wrapper around statsD client and logging. Its job is to capture Important metrics such as Latencies, Successful/Failed Messages Count, Sink Response Time, etc. for each record that goes through the Firehose ecosystem.
Commit
- SyncConsumer:
- In the Consumer thread, Firehose commits the offset after the messages are sent successfully .
- AsyncConsumer:
- In the Consumer thread, Firehose checks if any of the sink-pool tasks are finished. It sets the offsets of those messages to be committable. It commits the all the committable offsets.
Message Final State
The final state of message can be any one of the followings after it is consumed from kafka:
- Sink
- DLQ
- Ignored
- Filtered
One can monitor via plotting the metrics related to messages.
Schema Handling
Incase when
INPUT_SCHEMA_DATA_TYPE is set to protobufProtocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data. Data streams on Kafka topics are bound to a protobuf schema.
Firehose deserializes the data consumed from the topics using the Protobuf descriptors generated out of the artifacts. The artifactory is an HTTP interface that Firehose uses to deserialize.
The schema handling ie., find the mapped schema for the topic, downloading the descriptors, and dynamically being notified of/updating with the latest schema is abstracted through the Stencil library.
The Stencil is a proprietary library that provides an abstraction layer, for schema handling.
Schema Caching, dynamic schema updates, etc. are features of the stencil client library.
Incase when
INPUT_SCHEMA_DATA_TYPE is set to json- Currently this config is only supported in Bigquery sink,
- For json, in bigquery sink the schema is dynamically inferred from incoming data, in future we plan to provide json schema support via stencil.
Firehose Integration
The section details all integrating systems for Firehose deployment. These are external systems that Firehose connects to.
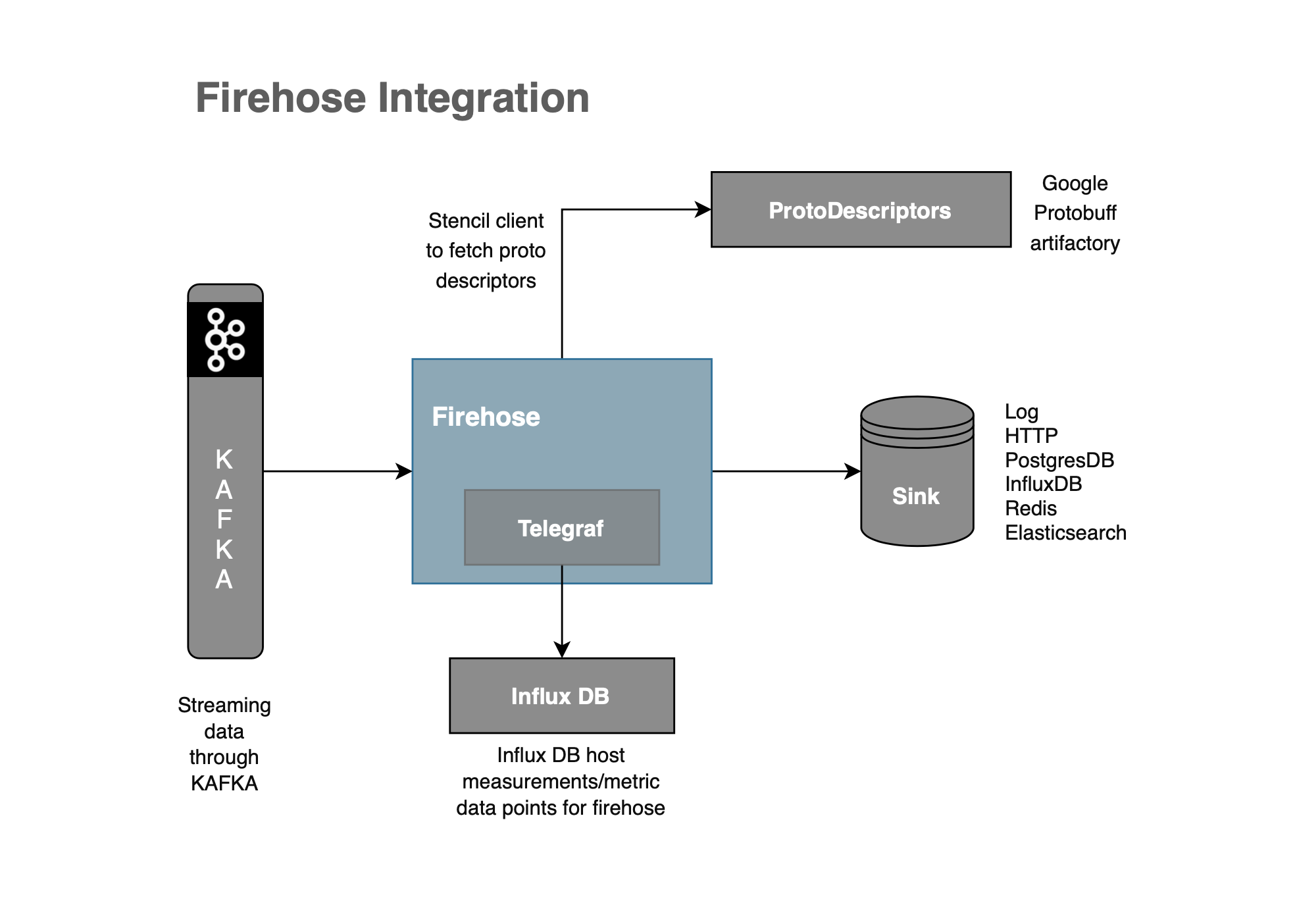
Kafka
- The Kafka topic(s) where Firehose reads from. The
SOURCE_KAFKA_TOPICconfig can be set in Firehose.
ProtoDescriptors
- Generated protobuf descriptors which are hosted behind an artifactory/HTTP endpoint. This endpoint URL and the proto that the Firehose deployment should use to deserialize data with is configured in Firehose.
Telegraf
- Telegraf is run as a process beside Firehose to export metrics to InfluxDB. Firehose internally uses statsd, a java library to export metrics to Telegraf. Configured with statsd host parameter that Firehose points.
Sink
- The storage where Firehose eventually pushes the data. Can be an HTTP/GRPC Endpoint or one of the Databases mentioned in the Architecture section. Sink Type and each sink-specific configuration are relevant to this integration point.
InfluxDB
- InfluxDB - time-series database where all Firehose metrics are stored. Integration through the Telegraf component.
For a complete set of configurations please refer to the sink-specific configuration.