Lifecycle
Architecturally after the creation of Dagger, it goes through several stages before materializing the results to an output stream.
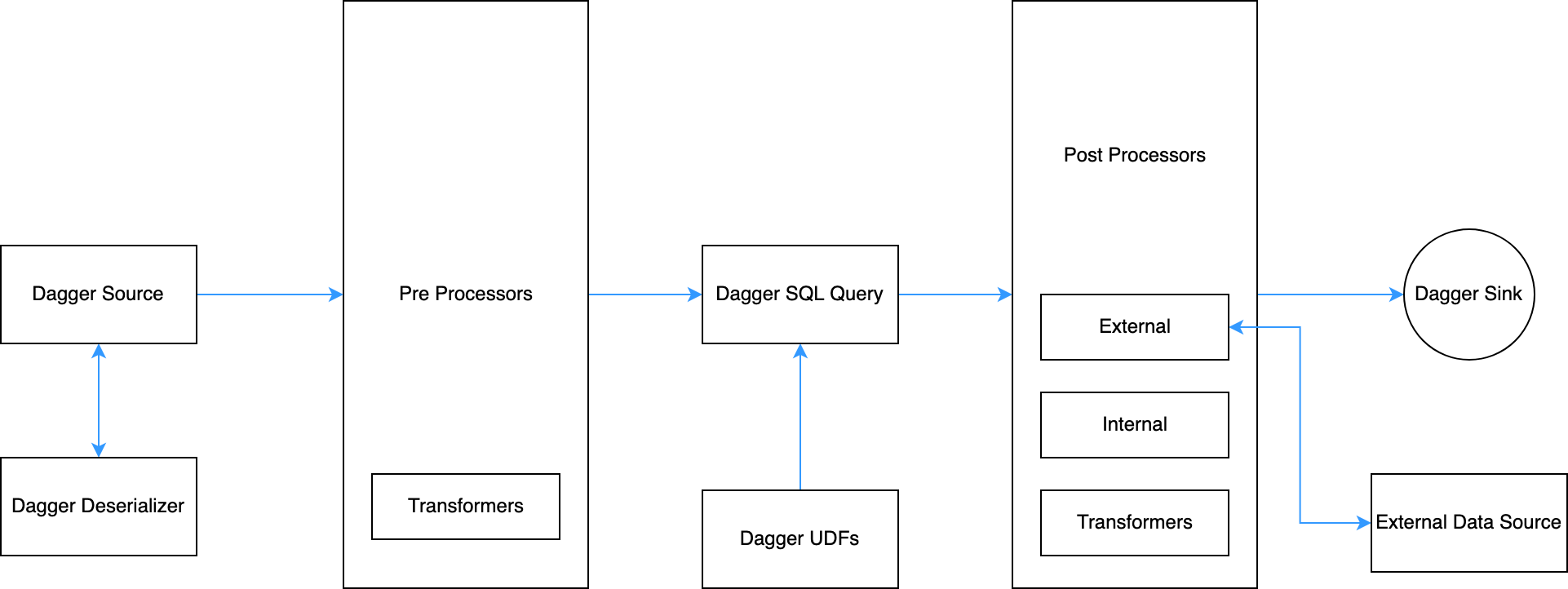
Stage-1: Dagger registers all defined configurations. JobManager validates the configurations and the query and creates a job-graph for the same.Stage-2: Data consumption from the source and its deserialization as per the protobuf schemaStage-3: Before executing the streaming SQL, Dagger undergoes a Pre-processor stage. Pre-processor is similar to post processors and currently support only transformers. They can be used to do some filtration of data or to do some basic processing before SQL.Stage-4: In this stage, Dagger has to register custom UDFs. After that, it executes the SQL on the input stream and produces a resultant Output stream. But in the case of complex business requirements, SQL is not just enough to handle the complexity of the problem. So there comes the Post Processors.Stage-5: In the fourth stage or Post Processors stage, the output of the previous stage is taken as input and some complex transformation logic can be applied on top of it to produce the final result. There can be three types of Post Processors: external, internal, and transformers. You can find more on post processors and their responsibilities here.Stage-6: In the final stage or sink stage, the final output is serialized accordingly and sent to a downstream (which can either be Kafka, BigQuery or InfluxDB) for further use cases.