Introduction
Welcome to the introductory guide to Shield! This guide is the best place to start with Shield. We cover what Shield is, what problems it can solve, how it works, and how you can get started using it. If you are familiar with the basics of Shield, the guides provides a more detailed reference of available features.
What is Shield?
Shield is a cloud-native role-based authorization-aware reverse-proxy service that helps you manage the authorization of given resources. In uses SpiceDB authorization engine, which is an open source fine-grained permissions database inspired by Google Zanzibar.
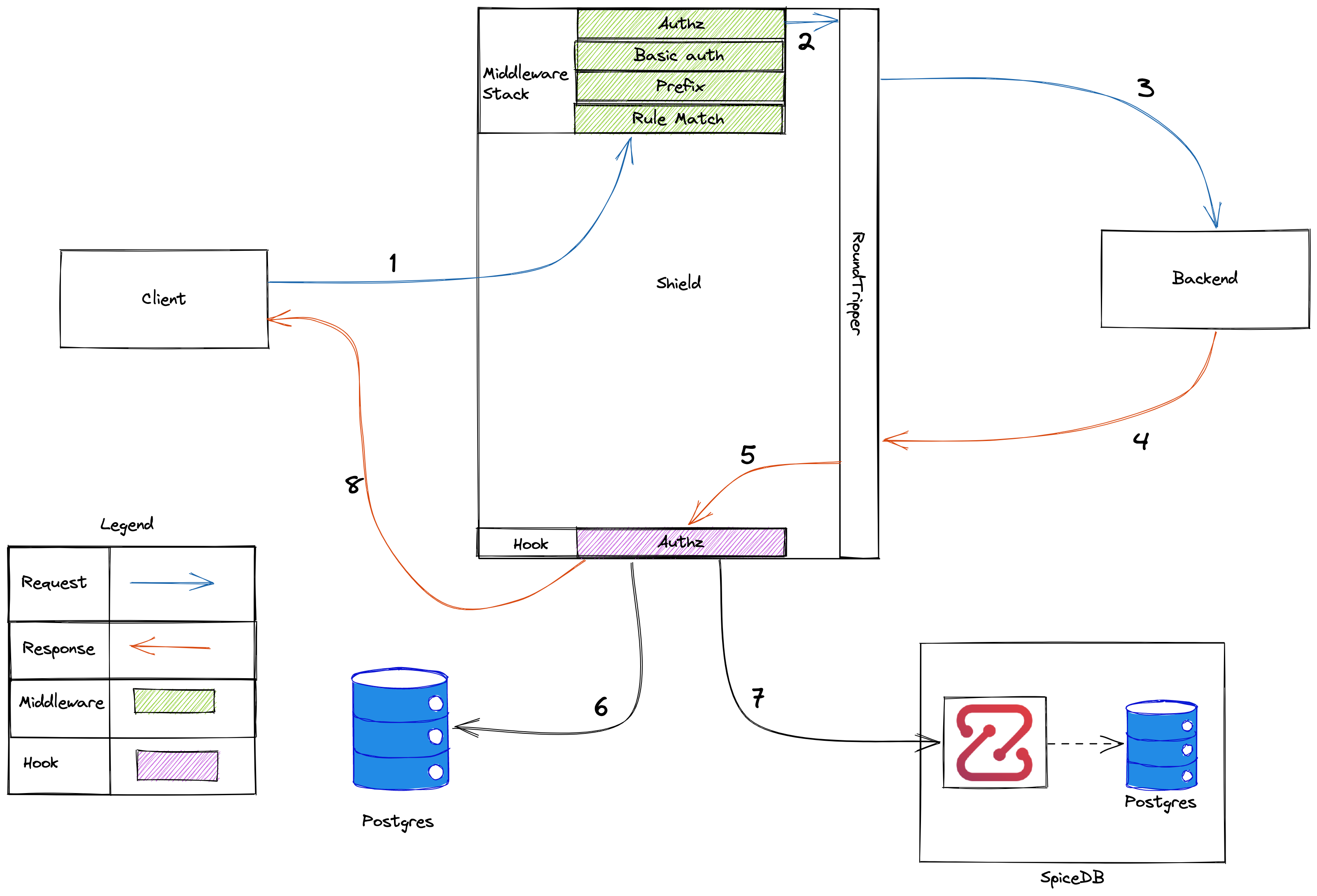
Shield being a reverse-proxy, intercepts the request between a client and the backend. It offers configurable authorization on each url path. This is handled by authz middleware. This is a non-mandatory step, and can be left unprotected as well.
A Resource Creation Hook comes handy when a resource needs to be created or updated in the backed. Shield keeps a record or the resource within it's database in order to check authorization later. The resource creation/updation request goes to the backend and when a successful response is received, the hook creates an instance of it in the database.
We can also configure role assignments to certian user or group on this resource as well during the resource creation.
We will talk more with example about the rule configuration in detail, in the guides.
How does shield work?
Here are the steps to work with Shield.
Configure policies: This step involes defition of resource types that will exist in the connected backend. User can also configure the roles and permissions that exist.
Configure rules: This step involves defining the authorization(via authz middleware) and resource creation(via hook) for each path in the backend.
Making Shield proxy request: User can now hit at the shield server followed by the url path.
Features
Organization and Project Management
Shield provides API to create and manage organizations/projects. Admins can create projects and groups within organizations.
Group Management
In group management, group admins can manage groups, add-remove members to the groups, and assign roles to the members.
Policy Management
Users can create policies to define which roles can perform what action on the resources.
Reverse Proxy
Shield can also restrict access to the proxy api to the users as per attributes and policies.
GRPC/REST based APIs
Using Shield
You can manage organizations, projects, group, users and resources in any of the following ways:
Shield Command Line Interface
You can use the Shield command line interface to issue commands and to perform the entire Shield features. Using the command line can be faster and more convenient than using API. For more information on using the Shield CLI, see the CLI Reference page.
HTTPS API
You can manage relation creation, checking authorization on a resource and much more by using the Shield HTTPS API, which lets you issue HTTPS requests directly to the service. For more information, see the API Reference page.